-
What is a narrow linewidth laser?
2022-07-05
-
What is the central wavelength of a laser?
2022-06-17
-
The principle of laser
2022-06-17
-
What are the types of fiber lasers?
2022-05-19
-
Reasons for high laser temperature
2022-05-19
-
How Lasers Work
2022-05-18
-
The history and current status of ultrashort pulse laser technology
2022-05-18
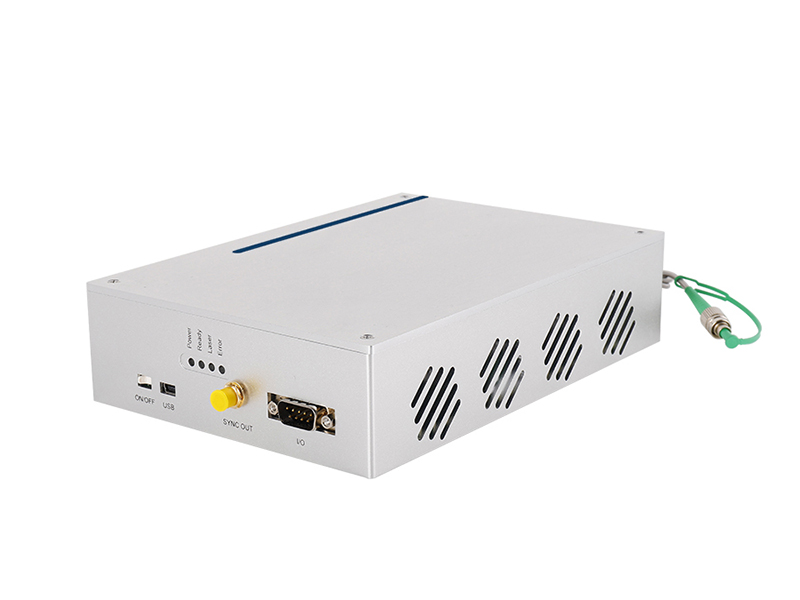
| Parameters | Units | Ablator-PNIR-30 | Ablator-PNIR-50 | Ablator-PNIR-70 |
| Working mode | Pulse | Pulse | Pulse | |
| Central wavelength | nm | 1064 | 1064 | 1064 |
| Maximum output power | W | >30 | >50 | >70 |
| PSO/POD function | Support | Support | Support | |
| Repetition frequency | MHz | 50-3000 | 50-3000 | 50-3000 |
| Pulse width | Ps | <10 | 10-15 | >15 |
| Number of pulses | 1-10 | 1-10 | 1-10 | |
| Polarization | Linear polarization | Linear polarization | Linear polarization | |
| Extinction rate | dB | >20 | >20 | >20 |
| Maximum single pulse energy | uJ | <350 | <350 | <350 |
| Beam quality | ≤1.3 | ≤1.4 | ≤1.5 | |
| Output spot diameter | mm | 2.0±0.3 | 2.0±0.3 | 2.0±0.3 |
| Power stability | % | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Pulse stability | % | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Output optical power adjustable range | % | 0-100 | 0-100 | 0-100 |
| Working environment | ||||
| Input voltage | VDC | 220 | 220 | 220 |
| Working temperature | ℃ | 20-30 | 20-30 | 20-30 |
| Storage temperature | ℃ | 0-60 | 0-60 | 0-60 |
| Power consumption | W | 1500 | 1500 | 1500 |
| Volume | mm | 738x506x195 | 738x506x195 | 738x506x195 |
| Weight | KG | 75 | 75 | 75 |
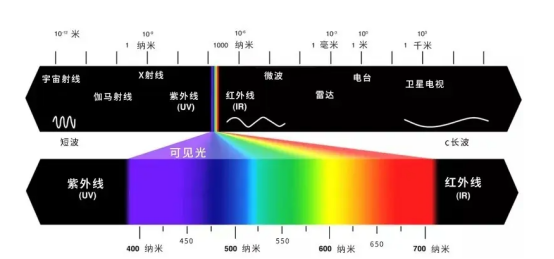
Center wavelength: refers to the output wavelength of the laser, which is an important parameter of the laser output laser beam. Different wavelengths represent different light sources as shown below:
Peak power: This is a special term for pulsed lasers and an important performance indicator of pulsed lasers. It represents the highest power that a single pulse can achieve. The unit is watt (W).
Pulse width: Abbreviated as pulse width, it refers to the duration of a single pulse. Therefore, it is a unit of time measurement, with various magnitudes such as milliseconds (ms), microseconds (us), nanoseconds (ns), picoseconds (ps), and femtoseconds (fs). The smaller the magnitude, the shorter the duration of the laser action.
Maximum single pulse energy (Pulse energy): refers to the laser energy carried by a single pulse. It is the product of peak power and pulse width. The unit is joule (J). For example, when the peak power is 10 kilowatts and the pulse width is 100 nanoseconds, the pulse energy E=10kW*100ns=1mJ.
Pulse repetition rate (Pulse repetition rate): Equivalent to the number of times a pulse repeats in one second. The unit is Hertz (Hz).
Output power (Average power): refers to the laser energy output per unit time in a repetition cycle. It is the product of pulse energy and pulse repetition frequency. The unit is watt (W).
Peak power density (Peak power density): refers to the laser power per unit area, an indicator determined by the laser power and the area where the laser acts. The unit is Watt/square centimeter (W/CM2).
Other important influencing indicators include: beam quality, divergence angle, spot roundness, spot diameter, etc.
Beam quality: The definition of beam quality includes: far-field spot radius, far-field divergence angle, diffraction limit multiple U, Strehl ratio, M2 factor, power on the target surface or ring energy ratio, etc.
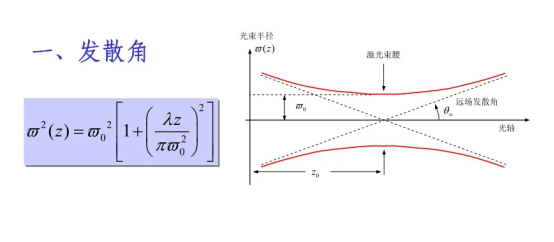
Divergence angle: The beam divergence angle is used to measure the speed at which the beam diverges from the beam waist to the outside. In free space optical communication applications, very low beam divergence is required. A beam with a very small divergence, such as a beam radius that is close to constant over a long transmission distance, is called a collimated beam.